ABSTRACT
Short backfire antenna has an enclosed structure with two reflectors on top of each other conventionally short backfire antenna is characterized by gain of above 10 dB, making it attractive for handheld radio monitoring and other man-portable applications. However, a microstrip patch fed short backfire antenna had a broad E-plane radiation pattern main lobe, leading to a loss of gain and low aperture efficiency. Using commercially available CST microwave software the aim of this project was to design a short backfire antenna which has symmetric E&H planes radiation pattern.
Adding six parasitic wires inside the cavity of a short backfire was found to narrow the E-plane radiation pattern main lobe, making it more like the H-plane radiation pattern and increasing the peak gain making it to around 15.5 dB. A single proof of concept antenna was built at 2.4 GHz with a microstrip patch fed with coaxial probe and have shown equalized principle planes.
LITERATURE REVIEW
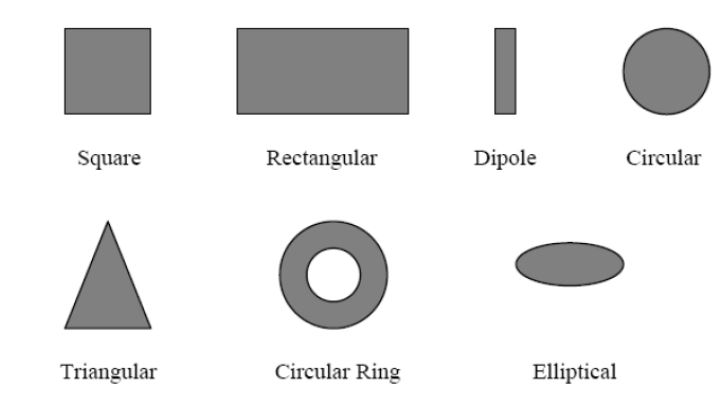
Figure 2.1 commonly used shapes of Microstrip patch antenna
The patch is generally made of conducting material such as copper or gold and can take any possible shape of the shapes shown in above figure 2.1 and also any other shape. The radiating patch and the feed lines are usually photo etched on the dielectric substrate. Microstrip patch antennas radiate primarily because of the fringing fields between the patch edge and the ground plane. Microstrip patch antennas have many advantages when compared to conventional antennas.
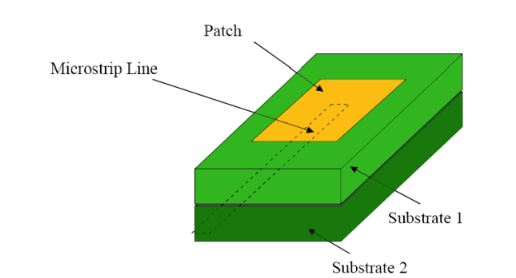
Figure 2.6: Proximity Coupled Feed
The microstrip antenna consists of a grounded substrate where a microstrip feed line is located. Above this material is another dielectric laminate with a microstrip patch etched on its top surface. Please note there is no ground plane separating the two dielectric layers. The power from the feed network is coupled to the patch electromagnetically, as opposed to a direct contact.
Source: University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Author: Ahmed Mohamed Madar
>> Microstrip Patch Antenna Project Report for Final Year Students
>> Project Report on Microstrip Patch Antenna for Engineering Students