ABSTRACT
Adhoc clustering in MANET is to divide mobile nodes into different virtual groups. Mobile nodes are allocated geographically adjacent in the cluster. Clustering is done by some rule specific in the network. In this paper, we have concentrated to modify weight based clustering algorithm to improve the performance in this wireless technology.
By slight improvement in existing weight based clustering algorithm reduction in cluster as well as cluster head can be observed through experiment. Proposed Algorithm specifies relaxing the weight criteria for isolated cluster head nodes in range of other cluster head as well as reconsidering the nodes in the range which is already participated in cluster formation. Reconsidering the participated node again in clustering formation could help in creation of better cluster, forming better routes as well as in conserving the cluster head energy.
RELATED WORK
The Ad hoc networks topology structure has classified into flat topology structure and hierarchical clustering structure. Due to the dynamic topology of ad hoc, the flat structure results are inefficient. After that, the researchers have proposed the hierarchical clustering structure for ad hoc networks. The clustering techniques can be classified as graph based and geographical based. A number of clustering algorithms have been proposed to choose cluster-heads based on the speed and direction, mobility, energy, position, and the number of neighbors of a given node.
PROPOSED WORK
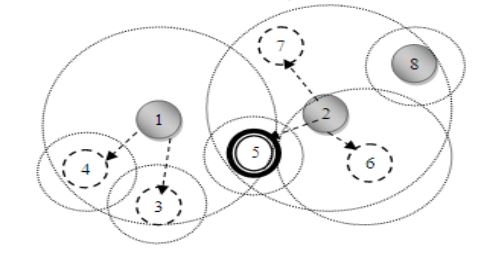
Fig 3: Cluster Formation with weighted clustering algorithm
Node_8 has no neighbors in the range and hence become isolated cluster as shown in Fig 3. We also assumed that cluster head can serve up to four nodes. In this case no cluster head is serving the maximum threshold. Here there are two problems isolated cluster head as well as maximum threshold has been not served. Both of the problems can be solved if relaxation is made in minimum weight criteria.
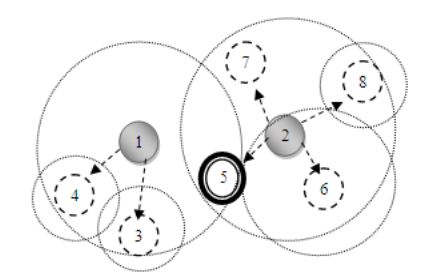
Fig 4: Cluster Formation after relaxing the minimum weight criteria for isolated nodes
It may take time and turn of next minimum node could be late in cluster head election process due to minimum weight. It will be an exception in the network with minimum weight having no neighbors become a member nodes instead a cluster head. Now the cluster formed will be shown in Fig 4.
SIMULATION ENVIRONMENT AND RESULTS
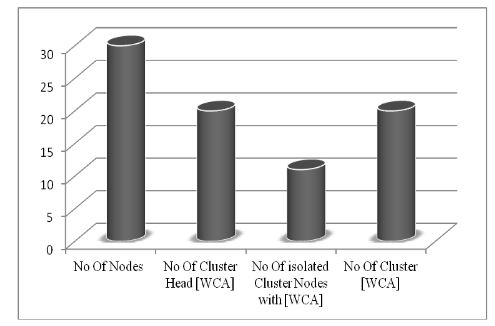
Fig 7: WCA implementation result
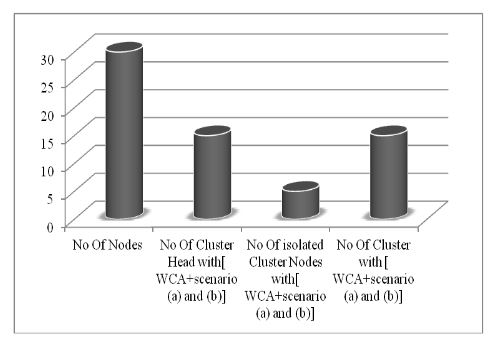
Fig 8: WCA implementation result after adding scenario(a) and scenario(b)
Fig 7 and Fig 8 shows the comparison between WCA and WCA with addition of scenario (a) and scenario (b). Since the network is designed randomly such scenarios are likely to take place. This research work has been focused on such issues and further modification to the algorithm for better result in some extra computation time. Computation cost will increase slightly but stability of cluster will increase too.
CONCLUSION
Relaxation in weighted clustering algorithm results in better cluster formation. Isolated Cluster head nodes become the cluster member for next selected cluster head due to minimum weight. Isolated node cluster head results due to minimum weight, coming prior in election of cluster head due to minimum weight selection as cluster head, also don’t cover any nodes in its range.
Since isolated node don’t deserve to be cluster he ad as it is not serving any nodes so it is better to become a cluster member for the next minimum weighted node. For saving the energy further relaxation required for member nodes or ordinary nodes in cluster formation process. Member nodes must join the cluster from which its distance is less from the cluster head. If cluster head covers the other cluster member in the range and it satisfy minimum weight as well as minimum threshold criteria, it must include in its cluster.
Practically it is proven fact that as distance from node increases transmission power is required more which results in more energy depletion. So if member nodes are located far from the cluster head it requires more energy to communicate and hence consume more power. So it can be observed by relaxing some of the criteria better cluster formation, energy efficient clustering can be achieved. These methods can be applied in all related weight based clustering to achieve more efficient clustering.
Source: Delhi Technological University
Author: Vijayanand Kumar
>> More Wireless Energy Projects for Engineering Students