ABSTRACT
Many routing protocols have been proposed for wireless sensor networks. These routing protocols are almost always based on energy efficiency. However, recent advances in complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) cameras and small microphones have led to the development of Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks (WMSN) as a class of wireless sensor networks which pose additional challenges.
The transmission of imaging and video data needs routing protocols with bot h energy efficiency and Quality of Service (QoS) characteristics in order to guarantee the efficient use of the sensor nodes and effective access to the collected data. Also, with integration of real time applications in Wireless Senor Networks (WSNs), the use of QoS routing protocols is not only becoming a significant topic, but is also gaining the attention of researchers.
In designing an efficient QoS routing protocol, the reliability and guarantee of end-to-end delay are critical events while conserving energy. Thus, considerable research has been focused on designing energy efficient and robust QoS routing protocols. In this paper, we present a state of the art research work based on real-time QoS routing protocols for WMSNs that have already been proposed. This paper categorizes the real-time QoS routing protocols into probabilistic and deterministic protocols.
In addition, both categories are classified into soft and hard real time protocols by highlighting the QoS issues including the limitations and features of each protocol. Furthermore, we have compared the performance of mobility-aware query based real-time QoS routing protocols from each category using Network Simulator-2 (NS2). This paper also focuses on the design challenges and future research directions as well as highlights the characteristics of each QoS routing protocol.
CATEGORIZATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF QUALITY OF SERVICE ROUTING PROTOCOLS
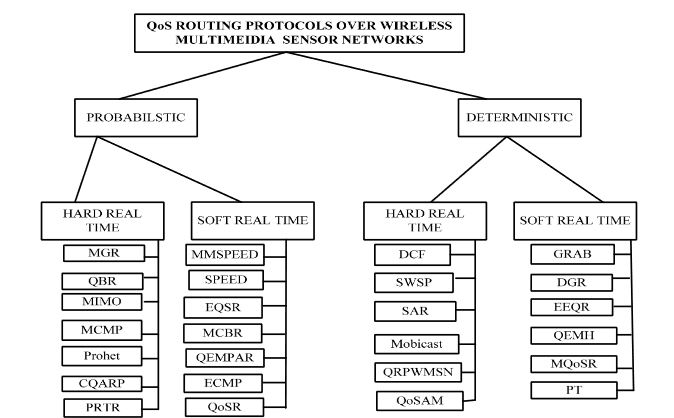
Figure 1. Classification of real- time quality of service (QoS) routing protocols
Based on the research issues, we have classified QoS routing protocols into two categories, which are probabilistic and deterministic, which in trun include soft real time and hard real time QoS routing protocols. This will help researchers choose the best QoS routing protocol according to the requirements of the application in order to reduce energy consumption and obtain better throughput as given in Figure 1.
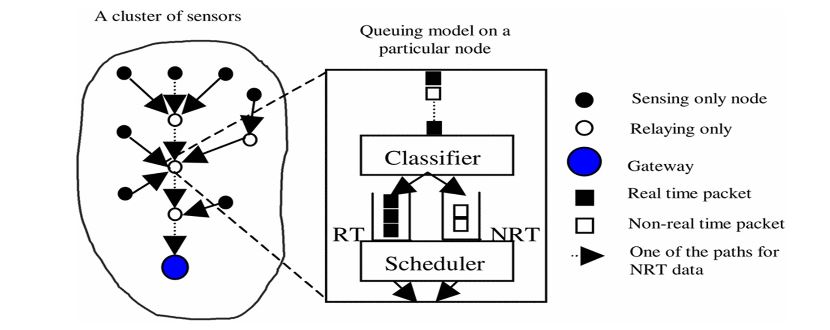
Figure 3. Queuing model in the cluster-based wireless sensor networks
All the nodes are basically assigned a similar bandwidth ratio, wh ich can create problems because some of the nodes require higher bandwidth. The strength of this protocol is to improve the throughput and prolong the network lifetime. Also, the issue of bandwidth assignment was resolved by using a different bandwidth ratio for each node. However, transmission delay was not considered, and the protocol also lacks mobility support. The working process of the protocol is depicted in Figure 3.
SIMULATION SETUP AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
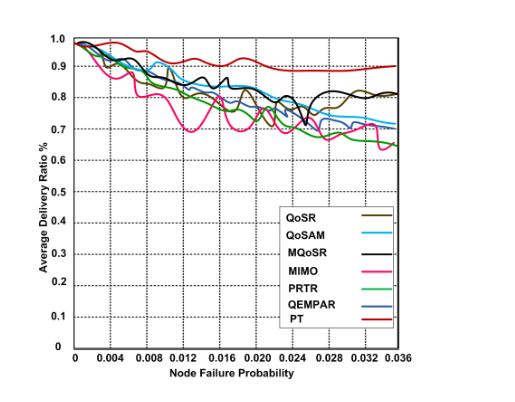
Figure 6. Average delivery ratios vs. different node failure probability
One of the significant metrics for evaluating the performance of the routing protocols is an average delivery rate. We compare the performance using the node failure probability and an average delivery ratio as shown in Figure 6. We observe that the performance of the routing protocols is comparatively similar, but PT shows slightly higher performance than other routing protocols because PT has the support of a least distance smart search model that helps find the shortest path.
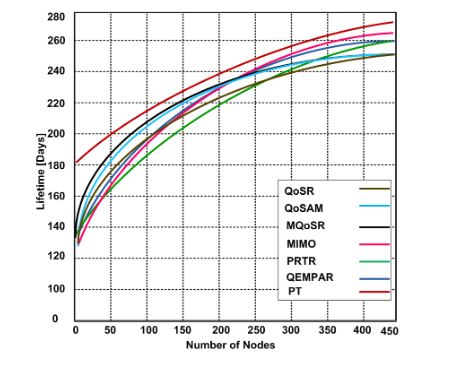
Figure 9. Network lifetime using different routing protocols and network size
The primary goal of the wireless multimedia sensor networks is to improve network lifetime because sensor nodes possesses limited power and other resources. In this experiment, we measured the performance of these routing protocols using different network sizes as depicted in Figure 9.
DISCUSSION OF THE RESULTS
Maintaining the real-time QoS parameters in the presence of mobility has been known to be one of the key challenges of WSNs and will continue to be a massive challenge for the deployment of WSNs because progression in battery technology has been slower than the progress in data communication rates and processing power. This challenge has appealed to several researchers to introduce real-time QoS protocols to balance the bandwidth consumption, packet loss, delivery rate, packet deadline, end-to-end delay and network lifetime.
CHALLENGES AND OPEN RESEARCH ISSUES
Most of the existing QoS techniques only support QoS-aware routing protocols. QoS-aware routing is a crucial part for maintaining the Quality of Service framework to improve the lifetime of wireless networks. The data delivery paths are analyzed using knowledge resource accessibility along with other requirements under QoS routing schemes. There are numerous issues that are to be focused on when designing the QoS routing protocols for WMSNs.
CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have conducted a comprehensive survey of QoS routing protocols in WMSNs. The QoS routing protocols are classified into deterministic and probabilistic categories. Further, both categories are classified into soft and hard real time protocols. We have highlighted critical challenges posed by the unique features of WMSNs. In addition, we have also reviewed QoS routing protocols with strength and weaknesses in WMSNs.
The paper also discusses the challenges and open research issues that will help the research community to deal with them in the future. In addition, we have simulated some known routing protocols using NS2 and also compared their performance. Finally, we have evaluated the characteristics of each routing protocol using several parameters.
Source: University of Bridgeport
Authors: Adwan Alanazi | Khaled Elleithy
>> More Wireless Sensor Networks Projects Abstract for Engineering Students
>> More Wireless Energy Projects for Engineering Students
>> More Wireless Projects Implementation in Ns2 for Engineering Students