ABSTRACT:
Ever since the creation of the first computers, humans have pondered the possibility of a computer capable of human-like thought and reason. Many sci-fi authors have explored the possibilities and consequences of a sentient computer and Artificial Intelligence. However, so far no one has managed to come close to an actual thinking computer.
This is possibly because the core structure of a computer is based on binary truths, “ones” and “zeros”, while the human brain does not work with only true or false.
This thesis presents the creation of an AI prototype called IKE. It is not an AI that can act like a human, but rather one that is a step closer to that final goal of a thinking computer. In this thesis, this is done by merging simulations of the five major senses with artificially created feelings, which are then fed into the system’s memory.
These are in turn embedded into objects and stored in the memory as instances of those objectsThe goal with this method is that when you give the system an object, it can tell you how it feels about the object and what experiences it associates with it. This is to give the computer a sense of simulated cognition which will allow it to answer in a human-like way.
The result of this work is a system that can be seen as an approach to an AI-complete system. It is an AI that has feelings and senses, as well as the ability to express them. However, it cannot gather or make up new feelings nor experience them in any way, as this is left for a future project to solve.
SNIPPETS:
Purpose:
The aim of this thesis is to present the development of a prototype of a partial AI-Complete system, including a model and an implementation thereof. That is, a system with some small semblance of digital cognition.
The model will be programmatically implemented in order to test that it truly works. The digital cognition will enable IKE to recognize an object and share its thoughts, memories, feelings and other knowledge of the object.
Goal:
The goal of this system is to provide results for researchers within the field of AI. A complete solution to any AI-Complete problems will not be given in this report, as it is meant to be a small step on the way to a solution.
This is done in order to implement what is known today, but more importantly to find out what is still missing before the AI-Complete problems can be solved and a truly sentient computer program can be created.
Methodology:
When taking on a project such as this thesis, choices regarding procedures to be used have to be considered very carefully. In many cases, these choices are made retrospectively, diminishing the effectiveness of the entire study. This part will cover the philosophical assumptions, research approaches and methods applicable to this type of project.
Quantity vs. Quality
To reduce the amount of actually applicable methods, a major choice to be made is whether to do quantitative or qualitative research . While these are fundamentally different to each other, they are not mutually exclusive. There is a third option, triangulation, which is a combination of the two.
Philosophical Assumptions
Once a type of research has been decided, the overall mind-set with which to go about gathering information, the philosophical assumptions have to be decided. The available options described next are positivism, realism, interpretivism and criticalism.
Artificial Intelligence:
Before to the topic of what has happened in the field of AI research and where it is now, a brief explanation of the Turing Machine introduced previously is in order. Of course, that is not all Alan Turing contributed with to the field of AI research.
AI-Complete:
When imagining what AI could become, it is easy to be drawn into imagining famous examples of advanced AI from science fiction movies and books such as HAL9000 from 2001: A Space Odyssey or the homicidal Skynet from Terminator. These were AI capable of thought on par with, or sometimes greater than, human intelligence.
The Senses of Artificial Intelligence:
Much of what has been mentioned above in terms of ongoing research is regarding cognition and consciousness and this is of course no coincidence. Especially the last example is closely related to this thesis as it describes a way in which senses could be simulated digitally.
METHODS
This is a chapter containing most of the methods relevant to theses in general. The Choices are made and explained in appropriate detail.
Possible Methods:
First for the list of the potential methods, because of the sheer number of methods only a brief explanation will be given for each of them. After an explanation on the various methods, more in depth explanations for our choices will be given. The different methods are covered in Research Strategies, Data Collection, Data Analysis, Quality Assurance and System Development Methods.
PROTOTYPING
In this chapter, the prototyping method and how it was applied for this project is explored. There are entire books dedicated to detailing the prototyping method, as such only the necessary explanations are given here. Following there is an explanation on how it has been applied, including each phase with subsequent steps. A list of the major problems encountered and their solutions is also included.
DEVELOPING IKE
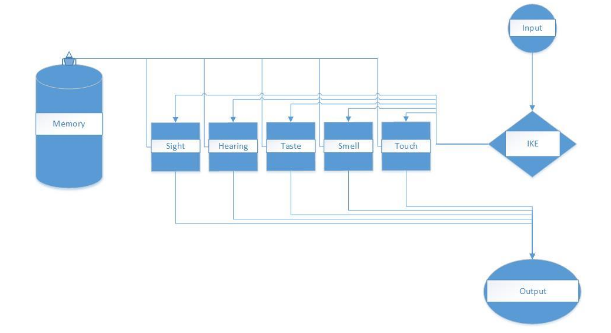
After the description of the prototyping process is a record of the creation of the prototype; the system IKE, which stands for Intelligent Kernel of Emotions. IKE is as already mentioned designed to be a small step towards achieving the dream of an AI-Complete system.
IKE
As already mentioned, the system was named IKE, the Intelligent Kernel of Emotions. The main reason for this being that the whole point with this project was to create an AI with the ability to possess emotions and senses, how they are connected rather than how they affect the actions of the AI.
In any case, the fifth chapter of this thesis IKE will be further explained in detail. First is a description of IKE and its feelings and senses. Following this, there is an explanation of the functionality these feelings and senses result in. Again, for the feelings to actually exist they have to be bound to memories, which in the case of IKE are represented as objects, but they might as well be occasions or specific points in time.
RESULTS
The seventh and second last chapter of the report evaluates the system in its current state, after all the work is done and the project is nearing completion. First is the evaluation as performed by the developers, followed by a summary of experiments with external subjects who got to try out IKE for the first time and their reactions.
CONCLUSIONS
The final chapter of this report summarises the project and tells what goals have been reached and how IKE relates to the previously mentioned related work in the field of AI and AI-Complete. Afterwards there is a discussion about the work that has gone into writing this report. Finally, the last paragraph of the report is about the future work and what remains before IKE can be considered an AI-Complete system.
FUTURE WORK
Now on to what is left before IKE can reach AI-Completeness. There is naturally a lot left, such as granting IKE a personality, but this part will focus more on things that could still be done with current technology. First is a brief look on the de limitations made in the initial chapter, followed by what is left for IKE and finishing up with what is actually attainable.
Source: KTH
Authors: Oskar Andersons | Filip Bark