ABSTRACT:
In recent years, technological developments have led to digital files being more easily distributed, for example through Napster (a file sharing service on the Internet). In order to manage and control the distribution of digital files, a new concept has been developed, called DRM (Digital Rights Management).
The purpose is to set every single file with individual rights that are extremely hard to break, and consequently make people pay and use the files legally. The file will then be fully protected from intrusion and alteration until the set rights expire.
The goal of this thesis is to look into and summarize DRM of today. We have concentrated on the mobile DRM market, and especially mobile phones. Especially the solutions applications that already exist and their functionality and properties, but also requirements regarding security levels, compatibility etc. We have also added predictions of the near future, ours as well as others.
Existing applications for DRM are well made but few are constructed for mobile phones. Mobile phones will however be a good and secure platform for DRM. At present there is no DRM application inserted in mobile phones in Europe. The third generation (3G) network will push the progress with the capability of broader bandwidth, with capacity of downloading more content to the phone.
Since the mobile phone software is embedded and the mobile phones are within a trusted network, the security level of a DRM application in a mobile phone can be discussed. A lower level of security would make it easier for managing content but also open up the market for hackers that wish to trespass. With a lower level of security you always have to consider the consequences and often it creates more problems than it solves.
We believe the DRM market and its value will increase exponentially over the next few years. The number of players on the mobile Internet DRM market will be less than on the Internet DRM market, due to the complexity of getting applications into the phone. The latter will consist of many more players, and remain fragmented, since it is an open market.
THE QUESTION AT ISSUE
Hypothesis:
“If Mobile phone developers can develop tools to protect content then this will
benefit providers and owners of the content!”
Questions:
- What are the differences between mobile Internet DRM and Internet DRM?
- How do the applications look today for DRM?
- Is an open DRM solution sufficient for the requirements of the mobile Internet?
(What level of protection is needed?) - How are the future aspects of the DRM development?
Limitations:
We will not make our own DRM application or establish which application that is working the best today or which would suit Sony Ericsson the best.
METHODS
Research:
We have chosen to make a qualitative research since we think that these scientific methods of working will suite our thesis. The qualitative approach can be said to involve five steps 2:
- Deducing a hypothesis
- Expressing the hypothesis
- Testing the hypothesis
- Examining the outcome
- Eventual modification of the theory and return to the first step
The qualitative research method often start with a very vague idea of the theory and examine the practical world to understand and further develop the theory.
The focus will not only be on our hypothesis but also on the questions and these components together will be the foundation of the research. We have used the questions to make the hypothesis clearer.
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT OF DRM
The first time DRM was introduced in the late 1980s. Some of the companies in the business existing today, were founded then and in the early 1990s. However most of today’s DRM companies came during the last five years.
The companies developing DRM come with many different technology backgrounds. Some originate from the security business. Two are well-known multinational companies (Microsoft, IBM). Many are spin-offs (i.e. Content Guard, from Xerox). Others come from the media area such as the entertainment, online industry, software licensing, pay TV, or publishing technologies (i.e. Adobe). Inter trust (1990) is one of the few pure DRM technology companies4.
Obstacles to DRM development:
There are a few obstacles that all could slow down or even stop the DRM market growth.
- Too many players.
- Partial solutions.
- Lack of expertise.
- Not enough clear legal precedent.
- Consumer reaction to content prising.
- Competing standards.
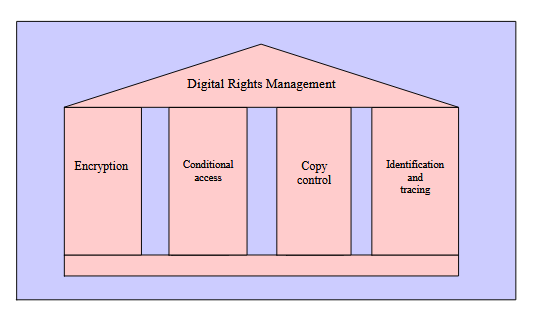
DRM – DIGITAL RIGHTS MANAGEMENT
Components of DRM:
The summary from all the different DRM descriptions is that a DRM system is supposed to enable secure exchange of copyright-protected digital media. DRM provides the ability for the content owner to distribute their content securely to authorised recipients, which gives them the control over the whole distribution chain.
DRM concepts:
A general DRM concept
The DRM market today is growing stronger and there are several different models of how to construct a DRM solution. The different solutions are often thought of as being used for different media contents.
The solution that we show (figure 5.2) here is a mix of a few of them, as an attempt to make it as general as possible. DRM has a lack of standards but the general concept is traceable through all the different applications, and that is what we have tried to catch.
Mobile Internet DRM vs. Internet DRM:
Internet DRM
Personal Computers (PC) are working as the device for Internet DRM. PCs are working as the platform for Internet for almost everyone here in Europe. This is the most common way of thinking of Internet.
Mobile Internet DRM
Mobile phones are working as the device for mobile Internet. The new high-rate networks that support General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) and Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) make it possible for the consumers to access a hole new kind of wireless data services which require a high data flow through the networks.
How they differ from each other
Mobile Internet and Internet are two different kind of platforms that can be used for DRM applications. DRM applications are needed for content protection. The platforms have different techniques for enabling content downloading from the Internet, which will be the main usage area for DRM.
DRM Applications
General information:
With no general DRM standard adopted, many companies have developed and marketed their own solutions. Currently there are twenty plus different applications available on the market. From the market’s perspective this is a good situation, the competition gets fierce and the development proceeds. Even though this situation also gains customers, it has a negative impact as well.
ANALYSIS AND RESULT
Survey:
In this part all the solutions along with their properties are evaluated. The major properties for the different 28 solutions (Reciprocal turned out to be out of business) that we have looked closer at are:
- Cryptography
- Watermarking
- Exists/used today
- Kind of content
- Mobile Internet
- Own created licenses
- Standards
- Client
- Other information
What Security Level is Required In A DRM System for Mobile Phones?
Protection can be looked at in two different kinds, first the protection that is in the object (cryptography and watermarking). That is an attempt to lock the protection to the content. The other one is protection around the object (DRM distribution chain, controlled access to content with playback protected). The difference is that if the protection in the object gets broken then only that object gets free.
CONCLUSION
When this project started, we did not have any knowledge of DRM. Along with the process we have learned more and more, and realized the complexity and size of the DRM business, which consists of companies from many different fields, e.g. content providers, software developers, mobile phone manufacturers, and operators.
With DRM being so new, there hardly exists any printed material, so we have mostly used Internet sources. Another aspect making this hard, is the definition of DRM; there are as many explanations of DRM as there are companies involved.
When comparing the mobile Internet with the Internet we found the sooner to be more secure and more suitable for DRM. It is not about choosing between the two; they are used for different purposes. DRM is a technique that is to be used on both platforms.We have looked into the existing DRM applications, and found that they are all different regarding content, protection mechanisms, target groups, platforms and clients etc.
The applications are generally well made, and a good foundation for the future, even though they are not widely used today. Mobile DRM applications are barely used today; hence it is hard to know how they function.
An Open DRM solution is sufficient for a mobile phone, it would meet the DRM requirements. However, we do not recommend it due to the high risk of attacks/hackers on high-value content. It is enough for low-value content though.
We believe the DRM market and its value will increase exponentially over the next few years. The “winner” will be the company providing most content. How technically advanced a solution is, does not matter as much, and consequently not the priority.
The number of players on the mobile Internet DRM market will be less than on the Internet DRM market, due to the complexity of getting applications into the phone. The latter will consist of many more players, and remain fragmented, since it is an open market.Through answering the questions together with researching the theory, we have concluded that our hypothesis is true.
A DRM solution has clearly showed to be able to handle content securely, leading to the content providers getting paid.Consequently if the mobile phone developers embed a DRM solution then the same outcome as mentioned above will occur.
When conducting future studies we can recommend things we did not have time to do, but nevertheless are very interesting. Find the best solutions and implement them in mobile phones to see how they would behave in a real environment, and eventually find the most suitable one.
Look closer into the protection techniques and see how a trusted network functions, to find out how secure it really is. These are our examples of future studies or theses building on our research.
Source: Blekinge Institute of Technology
Authors: Johan Bengtsson | Emma Hansson
>> More Wireless Embedded Projects for Engineering Students