ABSTRACT
Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol is one of the key network protocols that ensure Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) maintain high performance during communication. MAC protocol design plays an important role in improving the performances of the whole network. First, Wireless Passive Sensor Networks (WPSNs) and MAC protocols are introduced in this paper. Second, some existing MAC protocols are introduced.
Sensor MAC (S-MAC) protocol is analyzed and existing improved backoff algorithms are introduced. A new MAC protocol called Improved Sensor MAC (IS-MAC) is then proposed to solve the problem that the contention window (CW) during carrier sense is fixed in S-MAC protocol. IS-MAC protocol is able to adjust CW in terms of network load, so energy consumption can be decreased. Finally, according to the simulation results on NS2, the proposed protocol has better performance in terms of throughput and energy consumption.
RELATED WORK
There are several existing MAC protocols for WSNs, including the S-MAC protocol, the Timeout MAC (T-MAC) protocol, the Data gathering tree-based MAC (D-MAC) protocol, and the Berkeley MAC (B-MAC) protocol. The S-MAC protocol works with a periodic sleep/listening mechanism and a low duty cycle in order to reduce the energy consumption of nodes. Each node independently controls its working state and should be in sleep state as much as possible.
IS-MAC PROTOCOL
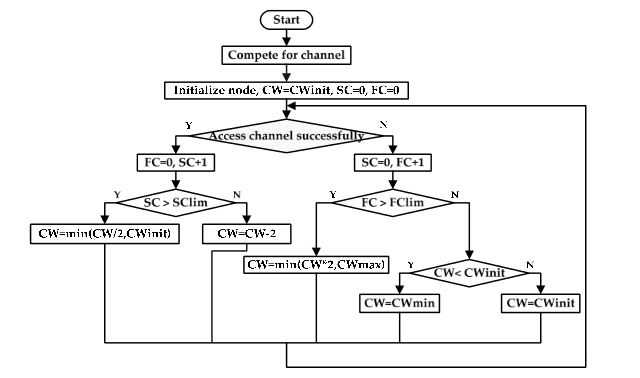
Figure 1. Flow chart for the improved backoff algorithm
When the number of continuous successful competition of channel is less than its corresponding threshold, the value of SC is less than SClim. The traffic load is relatively large right now, and the competition of channel is intense. Therefore, the current contention window merely requires minor adjustment, so it will be reduced by two to get the new contention window, CW = CW−2.The flow chart of this improved backoff algorithm is shown in Figure 1.
EXPERIMENTS AND ANALYSIS
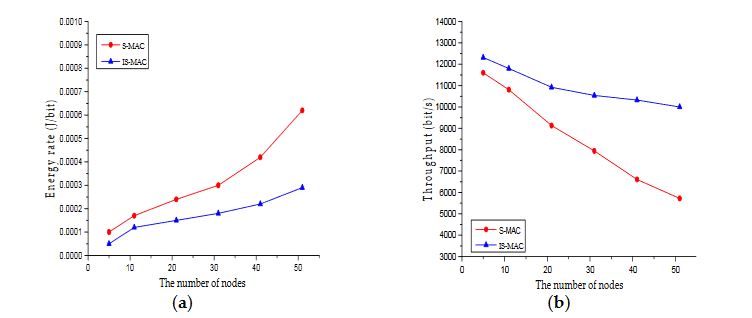
Figure 2. (a) Energy Rate of S-MAC protocol and IS-MAC protocol under different numbers of nodes
When the time interval is 1s, the energy rate and throughput of different numbers of nodes are compared. The time interval is chosen as 1s because at this time the channel competition is very intense and the superiority of the IS-MAC protcol is verified strongly. Figure 2 shows the curves of energy rate and throughput. The horizontal ordinate represents the number of nodes.
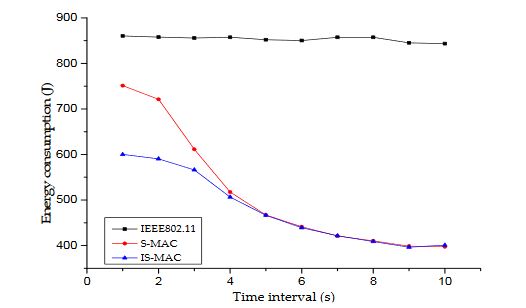
Figure 5. Energy consumption of sensor nodes under different loads
The vertical ordinate represents energy consumption and the horizontal ordinate represents time interval. The time interval changed from 1s to 10s and one point was taken every second. The results of energy consumption are shown in Figure 5.
CONCLUSIONS
WPSNs are developing rapidly in practical applications. A MAC protocol called IS-MAC was proposed for avoiding data collision in WPSNs based on a dynamically changing contention window. The proper contention window is computed for energy conservation according to the current network load. Meanwhile, this study introduced some parameters into the procedure of computing the contention window. Besides, this study verified the effectiveness of the improved algorithm on the NS2 platform. The simulation results show that the IS-MAC protocol can significantly outperform the S-MAC protocol in terms of throughput and energy consumption when the network load is heavy.
Source: Shandong University
Authors: Qingyao Yu | Guangming Li | Xiaojie Hang | Kun Fu | Tianqi Li
>> More Wireless Sensor Networks Projects Abstract for Engineering Students
>> More Wireless Energy Projects for Engineering Students
>> More Wireless Projects Implementation in Ns2 for Engineering Students